Copyright © Had2Know 2010-2026. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact
Site Design by E. Emerson
Cauchy Distribution Random Number Generator
The Cauchy distribution, also known as the Lorentz distribution or Cauchy-Lorentz distribution, is a fat-tail symmetric density function used to model processes in physics. The Cauchy distribution has no mean or variance; when you generate random variables from such a distribution, you will often encounter many extreme values.
The two parameters a and b are the location of the center (peak) and the scaling factor, respectively.
The probability density function is
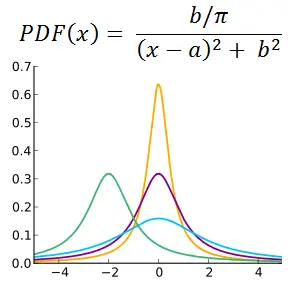
Since the Cauchy distribution is symmetric with a peak, the median and mode are both defined, and equal to a. However, the mean, variance, and skewness are not defined. If you set up the integrals necessary to compute these three statistics, the integrals will not converge.
The Cauchy distribution arises in the study of other distributions. For example, if Z and W are standard normal random variables, then the quotient Z/W has a Lorentz distribution with a = 0 and b = 1. Also, if X is a uniformly distributed random on the interval [0, 1], then tan(π(X - ½)) is a Lorentz random variable with a = 0 and b = 1.
The distribution also exhibits a self-transformation: If Y is a Cauchy random variable with a = 0 and b = 1, then the transformed variable
2Y/(1 - Y²)
is also a Cauchy random variable with a = 0 and b = 1.
© Had2Know 2010
