Copyright © Had2Know 2010-2026. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact
Site Design by E. Emerson
Error Function Calculator Erf(x)
The error function, denoted erf, is defined by the integral
erf(x) = (2/√π)∫xo e-t2 dt.
Erf(x) is closely related to the normal probability curve; the cumulative distribution function of a normally distributed random variable X is
CDF(X) = 0.5 + 0.5erf[(X-μ)/σ√2],
where μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation of the distribution. The error function integral cannot be evaluated in terms of elementary function, so one must use numerical algorithms. The error function is an odd function whose limit is -1 for negative values of x, and 1 for positive values of x. The function rapidly converges to its asymptotic values; erf(3) = 0.99998 and erf(-3) = -0.99998.
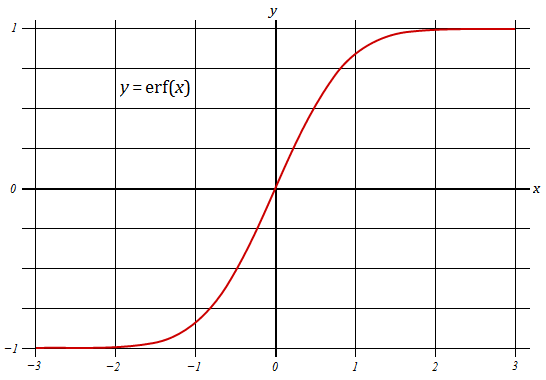
Properties and Equations
The values of x for which x = erf(x) are approximately 0.6175 and -0.6175. If you don't have access to an error function calculator such as the one above, you can approximate the function with the formula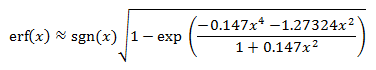
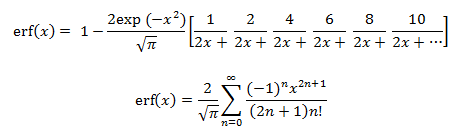
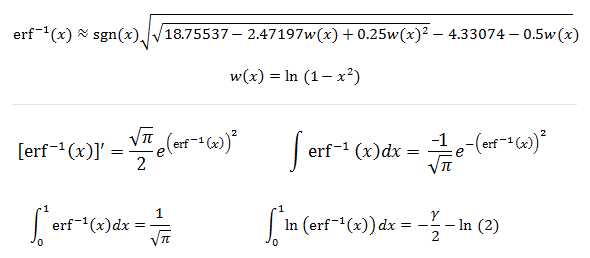
© Had2Know 2010
